Deep Generative Models
2024-25 Weekly Discussion Session II

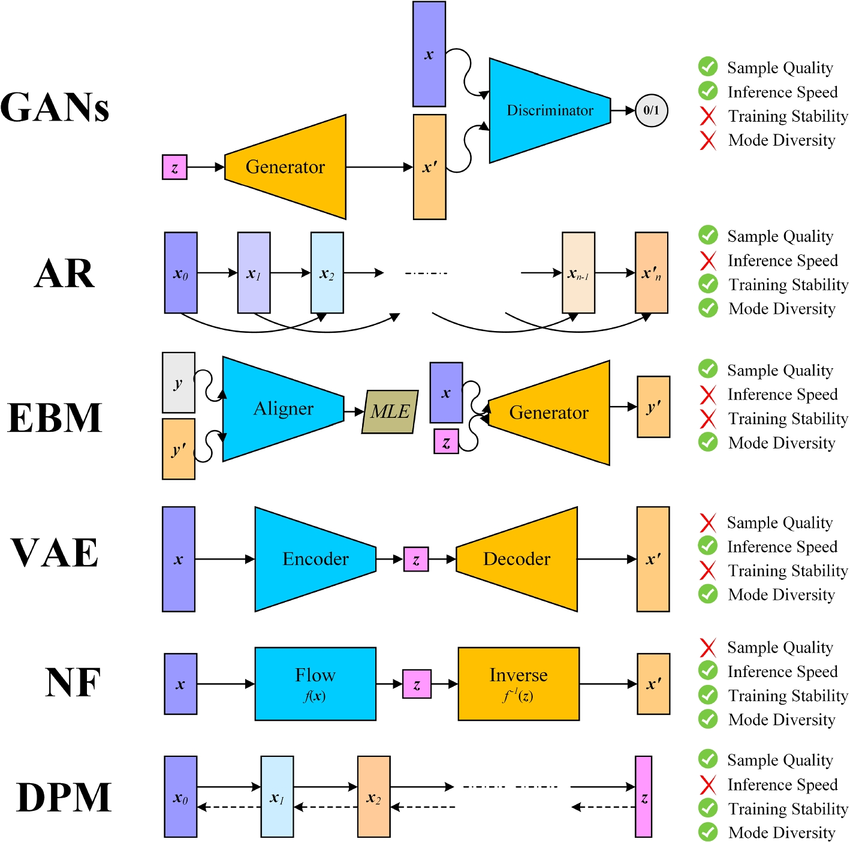

Discussion Theme: Deep Generative Model
Welcome to the our Session! It is designed to provide an in-depth exploration of one of the most exciting areas in machine learning. A deep generative model is a sophisticated deep learning approach that learns to generate new data by modeling the underlying probability distribution of a given dataset. It integrates mathematical concepts such as optimization and linear algebra, statistical techniques like probabilistic modeling and sampling methods, and methods in computer science to train deep neural networks capable of capturing complex patterns in data. These models are used in various industrial applications, including image synthesis and natural language processing. In fact, this paragraph was partially aided by a generative model -- showing just how useful these models can be!
Meeting Details
Time:
Every Saturday, 3:00 PM - 4:30 PM EST (online)
Zoom Link:
The Zoom link will be provided to Boil-MLC and SIAM members via SIAM slack group or email.
Language:
The discussion will be conducted in English.
Recording:
All sessions will be recorded and made available post-meeting on this page for members to review.
Discussion Guidelines:
At the beginning of each week, all regular participants will decide on papers to be discussed on Saturday so that we can read them during the week. The information of the events on the website will also be updated synchronously. If you have other ideas that you feel interested, you are entirely welcome to explore other papers on related topics and discuss it on our session meeting.
Session Schedule (updating synchronously)
Week 1 (Aug 31st, 2024): Introduction
- An introduction to Flow model, GAN and VAE.
Materials:
Week 2 (Sep 7th, 2024: A simple guide to Variational Autoencoder Model)
- VAE Architecture and Training: encoder-decoder structure, optimized by minimizing ELBO using the reparameterization trick.
- Variational Inference: approximates complex posteriors, balancing reconstruction loss and KL divergence.
- Advantages and disadvantages: generates smooth latent representations but may produce lower-quality samples and face challenges like posterior collapse.
Materials: